Digital Transformation
-


DevOps & RPA
-

Process Automation & Orchestration
-


Artificial Intelligence &
Machine Learning -


Metaverse and Web 3.0
-


Anywhere Workspaces
-


Big Data & Analytics
-


IOT
-


VR and AR
-

IT Infrastructure
Digital Transformation
Digital transformation approaches all aspects of a business, from its business models to customer experiences to processes and operations, with a customer-driven, digital-first mindset. It leverages data to drive intelligent workflows, faster and smarter decision-making, and real-time response to market disruptions using AI, automation, hybrid cloud, and other digital technologies. Finally, it alters customer expectations and opens up new business opportunities.While many organizations have embarked on a digital transformation in response to a single competitive threat or market shift, the goal has never been to implement a one-time fix. Digital Transformation is a continuous process to better enable a business to derive maximum output from IT infrastructure, this is done by learning, optimizing and reconfiguring - process, people and machine.

DevOps & RPA
DevOps
DevOps is the combination of cultural philosophies, practices, and tools that increases an organization’s ability to deliver applications and services at high velocity: evolving and improving products at a faster pace than organizations using traditional software development and infrastructure management processes. This speed enables organizations to better serve their customers and compete more effectively in the market.
Development and operations teams are no longer "silos" in a DevOps model. These two teams are sometimes combined into a single team in which the engineers work across the entire application lifecycle, from development and testing to deployment and operations, and develop a diverse set of skills that are not limited to a single function.


Quality assurance and security teams may become more closely integrated with development and operations throughout the application lifecycle in some DevOps models. When everyone on a DevOps team is focused on security, this is referred to as DevSecOps.
These teams employ practices to automate processes that were previously manual and time-consuming. They employ a technology stack and tooling that enables them to operate and evolve applications in a timely and dependable manner. These tools also help engineers independently accomplish tasks that normally would have required help from other teams.
RPA
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a software technology that facilitates the creation, deployment, and management of software robots that mimic human actions when interacting with digital systems and software. Software robots, like humans, can understand what's on a screen, complete the correct keystrokes, navigate systems, identify and extract data, and perform a variety of defined actions. However, software robots can do it more quickly and consistently than humans.
Workflows are streamlined by robotic process automation, making organizations more profitable, flexible, and responsive. By removing mundane tasks from their workdays, it also increases employee satisfaction, engagement, and productivity.
RPA is non-intrusive and can be implemented quickly to accelerate digital transformation. It's also ideal for automating workflows involving legacy systems that don't have APIs, virtual desktop infrastructures (VDIs), or database access.
Process Automation & Orchestration
Process automation is the act of replacing humans with machines when carrying out a series of tasks. In a business context, the term is commonly used to describe business process automation, in which software programs execute a set of activities within the modern, digital enterprise.
Process automation has a wide range of applications. Many businesses begin by automating basic support or departmental processes like data capture and expense approval. Others use advanced technologies to handle event-driven, mission-critical core business processes to automate more complex, cross-functional activities.

To automate various aspects of your business, you can use process automation software, software robots (or bots), and software scripts. A simple example would be the automatic routing of customer queries to the correct service agent. A more complex example might be using AI to create a short list of candidates for an open vacancy.
Process automation is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Businesses must monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of automation on a regular basis. This will increase your ROI. BPM monitoring is an excellent way to measure and compare the performance of business processes. It detects duplications and repetitive tasks, as well as problems that cause performance issues. Allowing you to take concrete steps to improve your situation and track your progress.
Process automation is a powerful technique, which can be applied in pieces or holistically. It delivers a raft of positives for any organization that implements it correctly. These include improved productivity, greater agility, improved customer experience, increased compliance, reduced costs, better utilization of staff and fewer errors.
Artificial Intelligence &
Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning represent a significant evolution in computer science and data processing that is rapidly transforming a wide range of industries.
As businesses and other organizations undergo digital transformation, they are confronted with an increasing flood of data that is both extremely valuable and increasingly difficult to collect, process, and analyze. New tools and methodologies are required to manage the massive amounts of data being collected, mine it for insights, and act on those insights once discovered.


In general, artificial intelligence refers to processes and algorithms that can simulate human intelligence, including cognitive functions such as perception, learning, and problem solving. AI includes machine learning.
Modern web search engines, personal assistant programs that understand spoken language, self-driving vehicles, and recommendation engines are examples of practical applications of AI.
It's no secret that data is becoming an increasingly valuable business asset, with the amount of data generated and stored worldwide increasing at an exponential rate. Of course, collecting data is pointless if nothing is done with it, but these massive amounts of data are simply unmanageable without the assistance of automated systems.
Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning enable organizations to extract value from massive amounts of data by providing business insights, automating tasks, and advancing system capabilities. AI/ML has the potential to transform all aspects of a business by assisting them in achieving measurable results such as,
• Increasing customer satisfaction
• Offering differentiated digital services
• Optimizing existing business services
• Automating business operations
• Increasing revenue
• Reducing costs

Metaverse and Web 3.0
Metaverse
The metaverse is a collective virtual shared space created by the virtual enhancement of physical and digital reality. Consider a metaverse to be the next evolution of the internet, which began as individual bulletin boards and independent online destinations. These destinations eventually became locations in a virtual shared space, similar to how a metaverse will develop.
A metaverse is neither device-agnostic nor owned by a single vendor. It is a self-contained virtual economy powered by digital currencies and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Metaverses, as a combinatorial innovation, require multiple technologies and trends to function. Virtual reality, augmented reality, flexible work styles, head-mounted displays, an AR cloud, the Internet of Things, 5G, artificial intelligence, and spatial computing are all contributing trends.


Web 3
Web3 is considered to be the Semantic Web which is intelligent, self sufficient and part of an open internet which employs AI and Machine Learning to function as a “global brain” and interpret content conceptually and contextually.
The semantic web is a development in online technology that enables people to produce, share, and connect material through search and analysis. Instead of using numbers and keywords, it is centered on word understanding. It uses machine learning and artificial intelligence. The result is the formation of Web 3.0 to grow smarter and more receptive to user demands.
Web3 makes peer-to-peer interactions the essence of a new generation of networked commerce and society. It retires centralized platforms, servers, and authorities as the key managers of information and value flows. Web3 will initially benefit large enterprises through applications that benefit from new blockchain-enabled business models and social and gaming networks. The first step for business and IT executives is to understand the keyways in which Web3 differs from Web 2.0, the early Web3 use cases and related technologies.
Web 3.0 leverages AI, Machine Learning and blockchain technology. It is expected to achieve real-world communication. Individuals will own the data, and they will be compensated for the time they spend on the internet. This sounds futuristic, and the data and privacy of the users will increase with the blockchain technology. Thus, if all goes well, Web 3.0 will be the future of the internet.

Anywhere Workspaces
Autonomous workspaces are the work paradigm of the future. The shift to remote work in 2020 clearly accelerated a long-term organizational shift to a hybrid work model. Some employees have returned to their workplaces, but many remain remote.
Implementing a hybrid work model also brings new challenges for IT, with 98% of IT organizations anticipating operational complexities. In supporting a distributed workforce, legacy tooling and manual IT tasks result in suboptimal experiences and poor security.
As a result, improving the operational efficiency of the IT organization has become a top IT priority for end-user computing teams. And this is where data-driven automation — i.e., autonomous workspaces — can help transform the IT workforce and achieve desired operational agility.

Big Data & Analytics
Big Data are high volume, high velocity, or high-variety information assets that require new forms of processing to enable enhanced decision making, insight discovery, and process optimization. It is a collection of massive data sets that conventional computing techniques cannot handle. The term encompasses not only the data but also the various frameworks, tools, and techniques involved. Technological advancement and the introduction of new channels of communication (such as social networking) and new, more powerful devices have presented industry players with a challenge in that they must find new ways to handle data.


The entire world had only five billion gigabytes of data from the beginning of time until 2003. In 2011, the same amount of data was generated in only two days. This volume was generated every ten minutes by 2013. As a result, it is not surprising that 90% of the world's data has been generated in the last few years. All this data is useful when processed, but it was largely ignored before the concept of big data emerged. With the development and increase of apps and social media and people and businesses online, there’s been a huge increase in data. If we look at only social media platforms, they interest and attract over a million users daily, scaling up data more than ever before. The next question is how exactly this huge amount of data is handled and how it is processed and stored. This is where Big Data comes into play.
And Big Data analytics has revolutionized the field of IT, enhancing and adding added advantage to organizations. It involves the use of analytics, new age tech like machine learning, mining, statistics and more. Big data can help organizations and teams to perform multiple operations on a single platform, store Tbs of data, pre-process it, analyze all the data, irrespective of the size and type, and visualize it too.
Big data analytics is the use of advanced analytic techniques against very large, diverse big data sets that include structured, semi-structured and unstructured data, from different sources, and in different sizes from terabytes to zettabytes. With big data analytics, you can ultimately fuel better and faster decision-making, modelling and predicting of future outcomes and enhanced business intelligence. As you build your big data solution

IOT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects—"things"—embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems via the internet. These gadgets range from common household items to sophisticated industrial tools. Experts predict that with more than 7 billion connected IoT devices today, this number will rise to 10 billion by 2020 and 22 billion by 2025.
IoT has emerged as one of the most important technologies of the twenty-first century in recent years. Now that we can connect everyday objects to the internet via embedded devices, such as kitchen appliances, cars, thermostats, and baby monitors, seamless communication between people, processes, and things is possible.
Physical things can share and collect data with minimal human intervention thanks to low-cost computing, the cloud, big data, analytics, and mobile technologies. Digital systems can record, monitor, and adjust each interaction between connected things in this hyperconnected world. The physical and digital worlds collide and collaborate.


While the idea of IoT has been in existence for a long time, a collection of recent advances in a number of different technologies has made it practical.
• Access to low-cost, low-power sensor technology. Affordable and reliable sensors are making IoT technology possible for more manufacturers.
• Connectivity. A host of network protocols for the internet has made it easy to connect sensors to the cloud and to other “things” for efficient data transfer.
• Cloud computing platforms. The increase in the availability of cloud platforms enables both businesses and consumers to access the infrastructure they need to scale up without actually having to manage it all.
• Machine learning and analytics. With advances in machine learning and analytics, along with access to varied and vast amounts of data stored in the cloud, businesses can gather insights faster and more easily. The emergence of these allied technologies continues to push the boundaries of IoT and the data produced by IoT also feeds these technologies.
• Conversational artificial intelligence (AI). Advances in neural networks have brought natural-language processing (NLP) to IoT devices (such as digital personal assistants Alexa, Cortana, and Siri) and made them appealing, affordable, and viable for home use.
As IoT becomes more widespread in the marketplace, companies are capitalizing on the tremendous business value it can offer. These benefits include:
• Deriving data-driven insights from IoT data to help better manage the business
• Increasing productivity and efficiency of business operations
• Creating new business models and revenue streams
• Easily and seamlessly connecting the physical business world to the digital world to drive quick time to value
Industrial IoT (IIoT) is the use of IoT technology in industrial settings, particularly for instrumentation and control of sensors and devices that use cloud technologies. Machine-to-machine communication (M2M) has recently been used in industries to achieve wireless automation and control. However, with the rise of cloud and related technologies (such as analytics and machine learning), industries can achieve a new level of automation, resulting in new revenue and business models. IIoT is also known as Industry 4.0 or the fourth wave of the industrial revolution.

VR and AR
Augmented reality is a technology that allows users to superimpose digital data on the real world. AR has been used for a wide range of purposes, including navigation, gaming, and education. While the most well-known applications of AR are found in mobile apps such as Pokemon GO and Snapchat, the technology is also being used in more practical ways, such as assisting surgeons in operating rooms and assisting engineers in product design. AR has nearly limitless potential applications, and the technology is rapidly evolving.
Virtual reality is a technology that immerses users in a realistic simulated environment. Users can immerse themselves in a virtual world by wearing a VR headset. Although virtual reality has been used for gaming and entertainment, it has the potential to be used for educational and training purposes as well. VR can, for example, simulate hazardous environments or situations such as a fire or a car accident. This can help people learn how to respond in an emergency without putting themselves in danger.


As businesses wake up to the potential of AR and VR, we're seeing more and more creative uses for the technology.
• Product Design and Development - AR/VR simulations can provide a realistic environment for testing products before they are built. Companies can understand how their products will work in the real world by creating a virtual product model. This is especially useful for products that are too costly or delicate to build prototypes of. AR/VR simulations can also help identify potential issues with a product before it is released to the public. Companies can avoid the expense and embarrassment of releasing a defective product by testing it in a simulated environment.
• Marketing and Advertising - AR and VR provide a unique opportunity to create truly immersive and interactive experiences that can captivate and leave an impression on an audience. These technologies are already being used in a variety of marketing applications, ranging from product demos to event promotions.
• Customer Service and Support - Businesses can use AR/VR to create a virtual environment in which customer service representatives can interact with customers in real-time, regardless of location. This not only reduces costs, but also improves the customer experience by allowing customers to get the assistance they require quickly and easily.
• Training and Education - VR is an incredibly powerful tool for training and education. It can provide realistic simulations of dangerous or difficult situations, allowing people to experience and learn from them in a safe environment. Moreover, VR is highly immersive, providing users with a level of engagement that is simply not possible with traditional methods such as books or lectures.
• Healthcare - Augmented and virtual reality has already begun to transform healthcare. These immersive technologies are being used for a variety of purposes, including training doctors and surgeons, providing remote patient care, and helping patients recover from injuries.
• Retail - Retailers are using AR/VR to create immersive shopping experiences for customers. By using AR/VR, retailers can provide customers with a realistic view of what products will look like in their homes. This can be especially useful for furniture and home decor retailers.
• Manufacturing - Workers can be guided through the assembly process step by step by overlaying digital instructions onto the physical product. If an issue arises with the assembly, AR/VR can be used to troubleshoot the problem and find a solution. AR/VR can also be used to plan production schedules and track inventory levels.

IT Infrastructure
On Premise Servers
In an on-premises environment, resources are deployed in-house and within an enterprise’s IT infrastructure. An enterprise is responsible for maintaining the solution and all its related processes. Enabling enterprises to retain all their data and are fully in control of what happens to it, for better or worse. Companies in highly regulated industries with extra privacy concerns are more likely to hesitate to leap into the cloud before others because of this reason. CBT recommends proper sizing and growth options to be considered, which is why we handle these requirements and share valuable insights with our customer.


On Premise Storage Solutions
On-premises storage is when data is stored on local hardware, such as servers, computers, or other devices. With on-premises storage, you own all the equipment, and you are responsible for both the maintenance and costs for your storage hardware. Businesses opt for on-premises storage solutions, as it can deter cybercriminals from trying to infiltrate your system and it can be used without connecting to the internet as it creates an internal network that is accessible anytime. CBT provides storage solutions based on the business and the data it stores. Our professionals looks at budget, business type, data type, backup options, capacity and scalability to determine the best option for you.
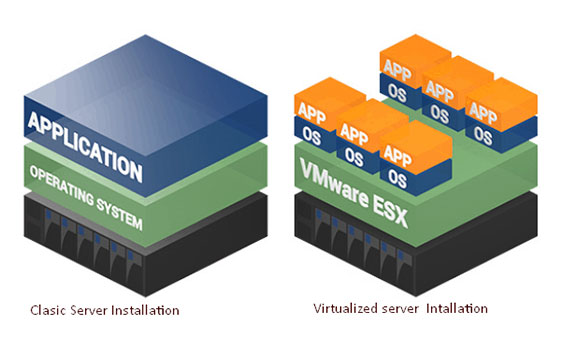
Virtualization Solutions
Virtualization solution is the process of creating a software-based virtual version of things whether that be computing, storage, networking, servers, or applications that behave just like their physical functionality. A virtualization solution is the method of creating multiple virtual environments within a single physical system, and these virtual environments are all using the hardware of the single physical environments. This virtualization solution is achieved by using a thin layer of software called a hypervisor. Hypervisor is software that creates the actual virtualization effect. It allows us to divide a physical system into many different and separated virtual environments, known as a virtual machine. The hypervisor allocates RAM, storage, and CPU power to each virtual machine as needed for more efficient hardware utilization. CBT’s expert technical team provides virtualization solutions that offer numerous advantages, including low or no-cost organization, full asset use, operational cost reserve funds and power investment funds.

Networking Solutions
A business network is to establish a stable connection between employees, customers, business partners and to important applications. CBT understands the importance of a business network and has helped enterprises in building cost-effective, high-performance networks for the past two decades. Effective information sharing and resource allocation helps organizations save money and increase productivity.
CBT Team specialized in managing both Managed and Unmanaged Switches that can effectively build you a high-performance network campus. We help you connect your business to the outside world, protect your information from security threats, and can even predetermine which computers get priority over others. CBT specialized in developing software-driven digital networking architecture which can evolve your organization beyond concepts of connectivity.
Our digital networking architecture can cover virtualization, security, compliance, insights, analytics and digital infrastructures. In addition to reducing your cost and complexity, bring your business scalability, manageability, and efficiency to your enterprise network.
Back Up Solutions
Data backup and information recuperation are significant pieces of maintaining a business. Contingencies must be put in place to mitigate the effects of PC frameworks crashes, human errors, and unforeseen systems failures. A business can reduce the amount of downtime by having information reinforcement frameworks set up. These data backup frameworks are practiced either by utilizing an offsite server or utilizing separate drives to store enormous measures of data. Without these information reinforcement frameworks set up, data backup turns into a risky circumstance where numerous organizations lose data when the most noticeably awful occurs. CBT defines the infrastructure required and creates a process to regularly back up data in a clean method to be able to recover any lost data in the least amount of time.
Colocation
A colocation facility, or colo, is a data center facility in which a business can rent space for servers and other computing hardware.
Typically, a colo provides the building, cooling, power, bandwidth and physical security, while the customer provides servers and storage. Space in the facility is often leased by the rack, cabinet, cage or room. Many colos have extended their offerings to include managed services that support their customers' business initiatives.
There are several reasons a business might choose a colo over building its own data center, but one of the main drivers is the Capex (capital expenditure) associated with building, maintaining and updating a large computing facility. In the past, colos were often used by private enterprises for disaster recovery (DR). Today, colos are especially popular with cloud service providers.
For some organizations, colocation might be an ideal solution, but there can be downsides to this approach. Distance can translate into increased travel costs when equipment must be manually handled and colo customers can find themselves locked into long-term contracts, which might prevent them from renegotiating rates when prices fall. It's important for an organization to closely examine their colo's service-level agreements (SLAs) so as not to be surprised by hidden charges.
Structured Cabling Solutions
Structured network cabling involves using a flexible and singular cabling infrastructure to connect multiple computers, phones and other devices together. Specialized sockets are provided for plugging in your multiple devices. A central communication network cabinet is provided for connecting multiple cables from different workstations. A well-designed and structured cabling system can help in addressing common workflow issues and network downtime problems effectively. CBT architects and designs streamlined cabling solutions for your office space to provide maximum connectivity and allowing for potential expansion.


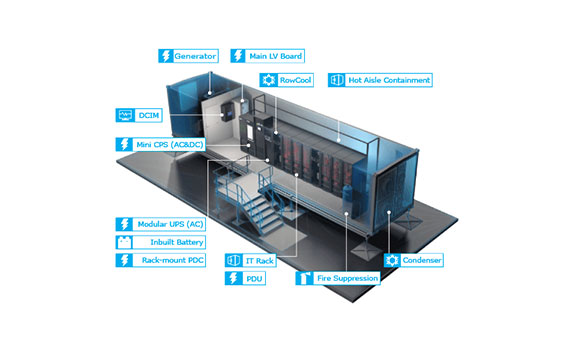
Data Center Racks and Accessories
Proper racking and stacking solutions are imperative, to enhance the systems flow of a computer room or IDF room or even a data center. CBT is capable of computational fluid dynamics (CFD), customized solutions for indoor and outdoor enclosures (IP rated and NEMA Rated). CBT also designs containment solutions with Cold aisle containment, hot aisle containment (CAC/HAC) or even with vented duct system (VED). Customization of cabinet sizes and their accessories can be designed and provided. CBT’s team of certified BICSI team RCDD and DCDC trained are able to ensure the project design is executed smoothly.
UPS Systems
An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is a piece of hardware that protects both your computer and your data against power outages. It acts as a backup power source in the event of a main power outage. Individual PCs can be protected by smaller UPS units, while bigger versions can power several devices or a full office. Individual UPS units are an option for small enterprises and should be sufficient to back up vital computers and other equipment required for business continuity. If you want to safeguard your company from the risks of unforeseen power outages, making sure you have the right UPS will save your business time, money and effort. CBT can provide experienced guidance on which hardware best meets your organizations requirements and train you how to properly use your ups, replace parts and train your team on the standard safety precautions.

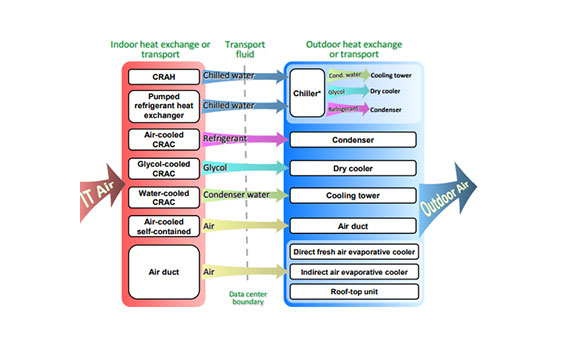
Cooling Systems
Computer room air conditioner and computer room air handler are two most common cooling system precision cooling and heat rejection equipment is used to collect and transport this unwanted heat energy to the outside atmosphere. CBT designs server cooling systems that improve efficiency and reduce the chance of server damage due to overheating.
Container Data Centers
Container Data Centers
CBT specializes at providing end to end requirement to build a containerized DC and take responsibility to build and manage it under their services portfolio. containerized DC are core to Oil and Gas industry, exploration industry and industries which required dedicated compute facility on premises.

CCTV and Security Systems
CBT provides hi-tech and customized security systems like CCTV security camera, IP Camera, Biometric Access Control & Time Attendance Systems, security alarm systems etc. We provide a wide variety of CCTV security cameras, Digital Video Recorders (DVR), Mobile DVRs, IP cameras, Network Video Recorders (NVR), wireless security cameras, surveillance camera systems with the necessary training required to operate them properly enabling you to safeguard your business effectively.
Wireless Solutions and Guest management with Lead Gen Analytics
Modern retailers and businesses have increased the demand for high-speed reliable internet for guest management and social marketing for retail sector and hospitality sector has increased manifold. Deep In-Store Analytics like Visitor Analytics, People Counting, Guest Wi-Fi Captive Portals & Wi-Fi based Analytics like Heatmaps, Zone Analytics to Launching New Experiences In-Store with Augmented Reality, Virtual Dressing Mirror and Makeup Try-Ons. CBT has both the track record and in-house ability to support your business. Our in-house team of Digital Technology experts use cutting edge technologies and proven tactics to create a winning formula for businesses, which provides customers with wonderful digital experiences that drive business and more importantly, provide a trackable return on investment (ROI) for our clients.

IP Telephony , VoIP and Collaboration
With work happening everywhere, both physically and digitally, people need a seamless experience from the home office and the desk all the way through to the board room. Enabling every employee with a full-featured, intuitive collaboration experience that allows them to message, meet, call, share content, and collaborate from any space is a foundational requirement for workplace transformation. CBT provides a platform that enables these key collaboration capabilities and interoperates with the productivity tools employees use every day so workstreams aren’t interrupted and people remain engaged and productive throughout the day.

